OpenVPN
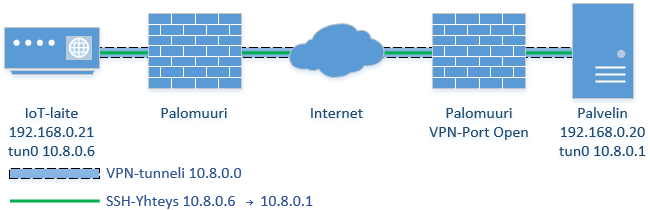
OpenVPN on avoimen lähdekoodin VPN-ohjelmisto, joka löytyy useimmista Linux-jakeluista. OpenVPN ei ole IPsec-yhteensopiva, joten se ei toimi kaupallisten ratkaisujen kanssa. Luodaan VPN-tunneli IoT-laitteen ja palvelimen välille.
Asennetaan OpenVPN ja easy-RSA ja puretaan konfiguraatio-tiedosto.
root@palvelin # apt-get install openvpn easy-rsa The following NEW packages will be installed: easy-rsa liblzo2-2 libpkcs11-helper1 opensc opensc-pkcs11 openvpn 0 upgraded, 6 newly installed, 0 to remove and 71 not upgraded. root@palvelin # gunzip -c /usr/share/doc/openvpn/examples/sample-config-files/server.conf.gz > \ /etc/openvpn/server.conf
Muutetaan salausavaimen bittisyys 1024 -> 2048 ja asetetaan OpenVPN käynnistymään rajatuilla oikeuksilla.
root@palvelin # vi /etc/openvpn/server.conf dh dh2048.pem user nobody group nogroupvi
Sallitaan IP forwarding, lisätään sertifikaatin vaatimat tiedot ja luodaan salausavaimet.
root@palvelin # vi /etc/sysctl.conf net.ipv4.ip_forward=1 root@palvelin # sysctl -p net.ipv4.ip_forward = 1 root@palvelin # cp -r /usr/share/easy-rsa/ /etc/openvpn root@palvelin # mkdir /etc/openvpn/easy-rsa/keys root@palvelin # vi /etc/openvpn/easy-rsa/vars export KEY_COUNTRY="FI" export KEY_PROVINCE="HM" export KEY_CITY="TOWN" export KEY_ORG="My Company Name" export KEY_EMAIL="antti@foo.bar" export KEY_OU="MyOrganizationalUnit" # X509 Subject Field export KEY_NAME="palvelin"
root@palvelin # openssl dhparam -out /etc/openvpn/dh2048.pem 2048 Generating DH parameters, 2048 bit long safe prime, generator 2 This is going to take a long time root@palvelin # cd /etc/openvpn/easy-rsa root@palvelin # . ./vars NOTE: If you run ./clean-all, I will be doing a rm -rf on /etc/openvpn/easy-rsa/keys root@palvelin # ./clean-all root@palvelin # ./build-ca Generating a 2048 bit RSA private key .....+++ ......+++ writing new private key to 'ca.key' ----- You are about to be asked to enter information that will be incorporated into your certificate request. What you are about to enter is what is called a Distinguished Name or a DN. There are quite a few fields but you can leave some blank For some fields there will be a default value, If you enter '.', the field will be left blank. ----- Country Name (2 letter code) [FI]: State or Province Name (full name) [HM]: Locality Name (eg, city) [TOWN]: Organization Name (eg, company) [My Company Name]: Organizational Unit Name (eg, section) [MyOrganizationalUnit]: Common Name (eg, your name or your server's hostname) [My Company Name CA]: Name [palvelin]: Email Address [antti@foo.bar]: root@palvelin # ./build-key-server server Generating a 2048 bit RSA private key ... Country Name (2 letter code) [FI]: State or Province Name (full name) [HM]: Locality Name (eg, city) [TOWN]: Organization Name (eg, company) [My Company Name]: Organizational Unit Name (eg, section) [MyOrganizationalUnit]: Common Name (eg, your name or your server's hostname) [server]: Name [palvelin]: Email Address [antti@foo.bar]: Please enter the following 'extra' attributes to be sent with your certificate request A challenge password []: An optional company name []: Using configuration from /etc/openvpn/easy-rsa/openssl-1.0.0.cnf Check that the request matches the signature Signature ok The Subject's Distinguished Name is as follows countryName :PRINTABLE:'FI' stateOrProvinceName :PRINTABLE:'HM' localityName :PRINTABLE:'TOWN' organizationName :PRINTABLE:'My Company Name' organizationalUnitName:PRINTABLE:'MyOrganizationalUnit' commonName :PRINTABLE:'server' name :PRINTABLE:'palvelin' emailAddress :IA5STRING:'antti@foo.bar' Certificate is to be certified until Aug 3 06:59:00 2027 GMT (3650 days) Sign the certificate? [y/n]:y ... 1 out of 1 certificate requests certified, commit? [y/n]y Write out database with 1 new entries Data Base Updated
kopioidaan sertifikaatit ja avaimet openvpn-hakemistoon ja käynnistetään OpenVPN.
root@palvelin # cp /etc/openvpn/easy-rsa/keys/{server.crt,server.key,ca.crt} /etc/openvpn root@palvelin # systemctl start openvpn root@palvelin # systemctl status openvpn ● openvpn.service - OpenVPN service Loaded: loaded (/lib/systemd/system/openvpn.service; enabled) Active: active (exited) since Sat 2016-08-05 10:20:53 EEST; 5s ago Process: 15173 ExecStart=/bin/true (code=exited, status=0/SUCCESS) Main PID: 15173 (code=exited, status=0/SUCCESS) Aug 05 10:20:53 palvelin systemd[1]: Started OpenVPN service.
Luodaan avaimet IoT-laitteelle ja kopioidaan avaimet ja sertifikaatit IoT-laitteelle.
root@palvelin # ./build-key client1 Generating a 2048 bit RSA private key ... writing new private key to 'client1.key' ... Sign the certificate? [y/n]:y ... 1 out of 1 certificate requests certified, commit? [y/n]y Write out database with 1 new entries Data Base Updated root@palvelin # cp /usr/share/doc/openvpn/examples/sample-config-files/client.conf \ /etc/openvpn/easy-rsa/keys/client.ovpn root@palvelin # mkdir keys/client root@palvelin # cp keys/{client1.crt,client1.key,client.ovpn} keys/client/ root@palvelin # cp ../ca.crt keys/client/ root@palvelin # cd keys/client/ root@palvelin # scp * antti@IoT:/home/antti/ antti@IoT's password: ca.crt 100% 1793 1.8KB/s 00:00 client1.crt 100% 5563 5.4KB/s 00:00 client1.key 100% 1704 1.7KB/s 00:00 client.ovpn 100% 3427 3.4KB/s 00:00
Kopioidaan sertifikatit, avaimet ja konfiguraatiotiedosto kotihakemistosta openvpn-hakemistoon. Lisätään sertifikaatit ja avaimet konfiguraatio-tiedostoon ja muokataan asetuksia.
root@IoT # cp /home/antti/{ca.crt,client*} /etc/openvpn/ ; cd /etc/openvpn/ root@IoT # echo '<ca>' >> client.ovpn ; cat ca.crt >> client.ovpn ; echo '</ca>' >> client.ovpn root@IoT # echo '<cert>' >> client.ovpn ; cat client1.crt >> client.ovpn ; echo '</cert>' >> client.ovpn root@IoT # echo '<key>' >> client.ovpn ; cat client1.key >> client.ovpn ; echo '</key>' >> client.ovpn root@IoT # vi client.ovpn ... remote palvelin 1194 ... user nobody group no group route 0.0.0.0 192.0.0.0 net_gateway route 64.0.0.0 192.0.0.0 net_gateway route 128.0.0.0 192.0.0.0 net_gateway route 192.0.0.0 192.0.0.0 net_gateway ...
Asennetaan OpenVPN ja nimetään client.ovpn -tiedosto client.conf -tiedostoksi, jos VPN-tunneli halutaan käynnistyvän automaattisesti käynnistyksen yhteydessä. Muussa tapauksessa VPN käynnistetään openvpn -komennolla. Jos yhteys muodostuu, tulisi laitteella näkyä tun0-verkkoliitäntä.
root@IoT # apt-get install openvpn The following NEW packages will be installed: easy-rsa liblzo2-2 libpkcs11-helper1 opensc opensc-pkcs11 openvpn root@IoT # openvpn --config client.ovpn root@IoT # ifconfig |egrep -A 2 tun0 tun0 Link encap:UNSPEC HWaddr 00-00-00-00-00-00-00-00-00-00-00-00-00-00-00-00 inet addr:10.8.0.6 P-t-P:10.8.0.5 Mask:255.255.255.255 UP POINTOPOINT RUNNING NOARP MULTICAST MTU:1500 Metric:1
Testataan yhteys ottamalla ssh-yhteys palvelimelta IoT-laitteelle.
root@palvelin # ssh antti@10.8.0.6 antti@10.8.0.6's password: The programs included with the Debian GNU/Linux system are free software; the exact distribution terms for each program are described in the individual files in /usr/share/doc/*/copyright. Debian GNU/Linux comes with ABSOLUTELY NO WARRANTY, to the extent permitted by applicable law. Last login: Sat Aug 5 11:55:40 2016 from 10.8.0.1 antti@IoT $
Jos VPN-tunnelia käytetään esimerkiksi IoT-laitteen hallintaan, kun SSH Port Forward -esimerkissä, niin OpenVPN:n kanssa tulee ottaa huomioon, että OpenVPN jakaa koko verkkoavaruuden. Tällöin tulisi huolehtia palveluiden rajaamisesta palomuurin avulla, esimerkiksi iptables.
![]()
