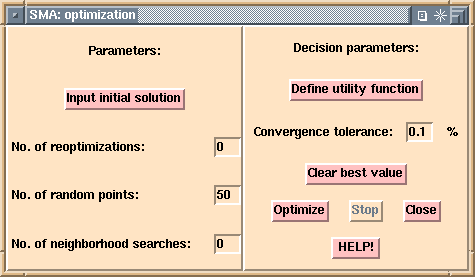
The optimization requires an initial solution from which the algorithm
starts improving step by step. This button brings up a window that lets
the user specify the initial solution using slide bars.
See an example of the iterations by the Hooke
and Jeeves direct search algorithm.