The child as an agent of change in kindergarten situations
Jyrki Reunamo
Helsinki University
Department of Teacher
Education
Research methods
1. Interview:
15 questions, Classification of answers according to who is changing, the child or also the environment. Child adapts himself/herself or also the environment
2. Observation:
Kindergarten setting
Child’s activity
Child changes/is changed
Child’ object of observation
Nearest child contact
3. Teachers’ evaluation of children
4. Parents’ evaluation of their children
1. Let’s think that you are playing and somebody else is having the toy you want. What do you do?
| Adapts him/herself | Adapts the situation |
|
|
2. What do you do when you are playing and somebody comes to disturb you and interrupt your play?
| Adapts him/herself | Adapts the situation |
|
|
6. Think of a situation when teacher comes to interrupt and stop your play. What do you do then?
| Adapts him/herself | Adapts the situation |
|
|
11. Think of a situation that you're work fails and you don't succeed. What do you do?
| Adapts him/herself | Adapts the situation |
|
|
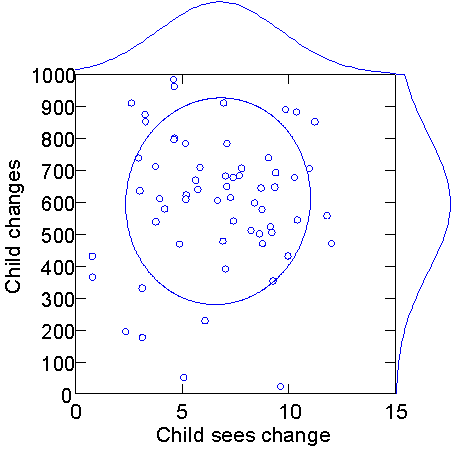
Child sees the change/child changes the situation

The interview: "child sees the possible change of the situation" correlates with
The observation: "child changes the situation"
0.043
Principal components: 2 factors’ solution
| The child adapts in the situation | The child also adapts THE situation |
| System seeks equilibrium | System seeks contact |
| Internally coherent system | Internal and external keep in contact |
| The reality exists | The reality depends on perception |
| Man has to study the laws of reality | Man has to test and develop reality |
| Man has to know how to use his tools | Man has to develope his tools |
| Child is independent and self-regulative | The situation determines interdependence |
| Learning: Metacognitive skills and selfreflection are highlighted | Learning: Practice of testing possibilities |
| Teacher: gives ideas, is a model and facilitator of kognitive conflicts | Teacher: When a teacher sees the child as a reality developer, she/he can help the child to become one |