Erikoisharjoitus II Luennoitsijan esimerkki Special assignment II, lecturer's example
Valitsin testimetsää Kuivajärven luonnonhoitometsästä
läheltä pistettä (2514865, 6860960, 192). Ilmakuvilta mitatut
puut ovat ko. alueella pitkiä. KUVAMITT-ohjelmalla, käyttäen
hyväksi lidar-DTM (HyderLidarDTM.hdr) sain puiden pituuksiksi pituuksiksi
24-32 m. Latvusten leveys vaihteli välillä 2-7 m. I selected a test site in the Kuivajärvi old growth
around the point (2514865, 6860960, 192). Using the photogrammetric observations
and the lidarDTM I estimated that tree heigts range from 15-32 m and the
crown widths from 3 to 7 m (see aerial view below) .
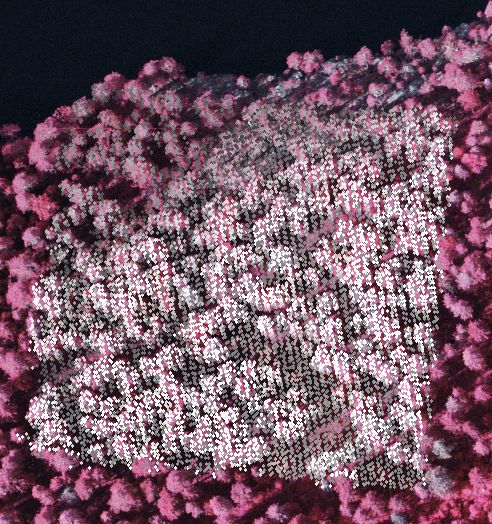
Kuva: Annetun pisteen ympäriltä ilmakuvalle 0440302 projisoidut
lidar-pisteet. Kohdealue jää kahden risteävän lidar
linjan (strip) alle, skannauskulmien ollessa noin 10-13o ja ±
1o. Test area seen in aerial image 0440302
with lidar points superimposed. The gery level indicates elevation with a
linear scaling between 185 and 215 m. The area is under two lidar strips
(perpendicular) with scan angles from 10 to 13 degrees and ±
1 degree.
Yo. kuvassa lidarpisteiden, first ja last, harmaasävy skaalattiin
välille Z = (185...227 m) » (0...255) ao. koodiriveillä
osiossa. Code changes in KUVAMITT for producing the
figure above:
Aliohjelma, jolla kuva tuotettiin: Private Sub plot_als_bin_file_Click()
pu_z = 255 - (185 - LP.Zs) * 6
If pu_z > 255 Then pu_z = 255
If pu_z < 0 Then pu_z = 0
Apu_z = pu_z
Form1.Picture1(i).DrawWidth = 3
Call r_transform_ground_to_pixel(i, LP.Xs,
LP.Ys, CDbl(LP.Zs), p_x, p_y)
Form1.Picture1(i).PSet ((p_x ....litania puuttuu........ - 1), RGB(Apu_z, Apu_z,
Apu_z)
If LP.Zf > 10 Then
pu_z = 255 - (185 - LP.Zf) * 6
If pu_z > 255 Then pu_z = 255
If pu_z < 0 Then pu_z = 0
Apu_z = pu_z
Call r_transform_ground_to_pixel(i, LP.Xf,
LP.Yf, CDbl(LP.Zf), p_x, p_y)
Form1.Picture1(i).PSet ((p_x ....litania puuttuu........ - 1), RGB(Apu_z, Apu_z,
Apu_z)
End If
Lidar pisteet tiedostoon Lidar points into
an ASCII-file
Seuraavaksi kirjoitin ko. alueen pisteet ASCII tiedostoon. Keskipiste on lähellä
"KKJ-hehtaarin" keskipistettä; otin koko hehtaarin pisteet talteen rajaamalla
3D pisteen (fotogrammetrinen ratkaisu) ympärille 150 x 150 m alueen
ao. lauseilla Plot_als_bin_file_Click() -aliohjelmassa: As the next step I had the lidar points written into an
ASCII-file. Following two lines were altered in the Plot_als_bin_file_Click()
-subroutine. Recall that (X_sol, Y_sol, Z_sol) is the 3D photogrammetric
point solution that can be set or measured from the images.
If Abs(LP.Xs - X_sol) < 75.5 And Abs(LP.Ys - Y_sol) <
75.5 And Abs(LP.Xf - X_sol) < 75.5 And Abs(LP.Yf - Y_sol)
< 75.5 Then
If Abs(LP.Zs - Z_sol) < 100 Then
Saman aliohjelman alkuun lisäsin lauseen, jolla avattiin ASCII-tiedosto
tulostusta varten In the same routine, a line of code
was added for opening the ascii-fle for output.
Open "c:\data\lidar_pisteet_LH_metsa.txt" For Output As 6
Aliohjelmaan laitoin ennen For i = 0 to NumOfImages -lausetta rivin tulostusta
varten; talteen menee koko pulssin sisältö, yhteensä 18 muuttujaa
per pulssi: In the same routine, just before the statement
For i = 0 NumOfImages, I added a line of code for printing the full contents
of the lidar-pulse into the ascii-file.
Print #6, LP.GPS_time, LP.omega, LP.phi, LP.kappa, LP.Xl, LP.Yl, LP.Zl,
LP.Scan_angle, LP.Xf, LP.Yf, LP.Zf, LP.Intf, LP.Rangef, LP.Xs, LP.Ys, LP.Zs,
LP.Ints, LP.Rangel
Aliohjelman loppuun tarvitaan tiedoston sulkeva lause And finlly, in the end of the rouine I added a line of code
that closes the ascii-file.
Close (6)
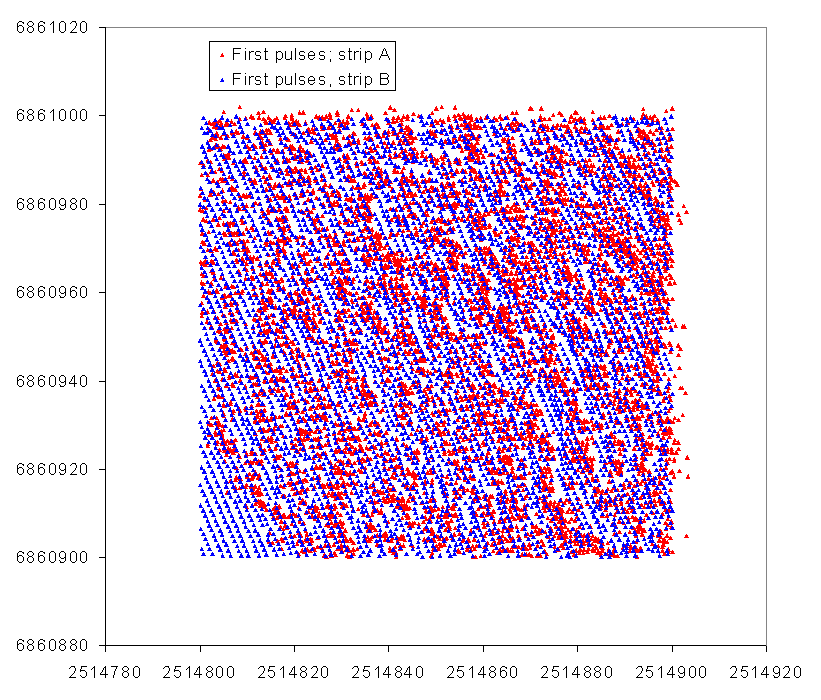
Kuva: Yhden hehtaarin first return -pisteet (LP.Xf, LP.Yf) tasossa.
Skannauskulman vaikutus tulee esille pisteiden XY-jakaumassa. Huom! kuinka
havaintoja on ko. hehtaarin ulkopuolelta - pulssi on "sijoitettu siihen
hehtaariin", johon last return -piste osui! Lidar data
covering one hectare (recall that the lidar data is stored in one hectare
files, checkboard-style). First return pulses as an XY map. Data from the
two strips is shown in different color and the effects of the scan angle
("oblique viewing") are seen in the two point patterns.
Referenssipuut Reference data
Mittasin 321 puuta ilmakuvilta pisteen (2514865, 6860960, 192) ympäristöstä;
pyrkien paikantamaan kaikki kuvilla näkyvät
puut. Mittaukset tein 04403 kuvilta, jotka on otettu 2 viikkoa ennen
lidar-dataa. Mittasin yhtenäisen alueen, joskaan en koko hehtaaria.
I positioned by manual multiple image-matching, using
three images from flight 04403, a total 321treetops in the neighborhood of
the center point. A whole/unbroken area was covered, however not the full
one hecrate area for which the lidar data is.
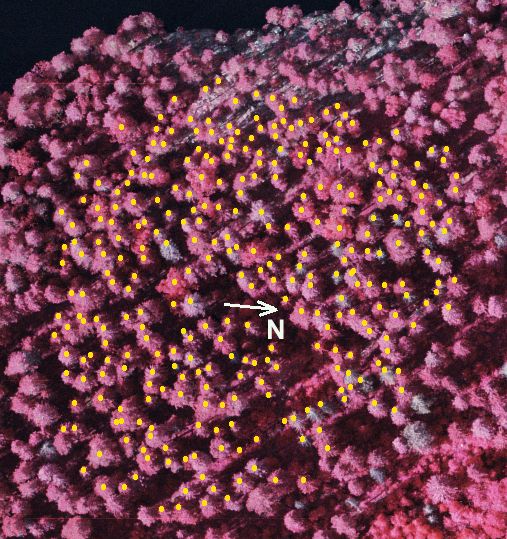
Kuva: referenssiaineistoksi (latvapisteet) mitatut pisteet projisoituna
ilmakuvalle 0440302. Maasto laskee kohti järven rantaa kuvan ylälaidassa.
Järven pinta on noin 141 m m.p.y (N60) ja maaston korkeus nousee 165
m. Rannassa (ylh. oik) on myös jyrkkiä rantakallioita, joilla
kasvaa harvaa mäntymetsää. The reference
tree tops seen in the aerial image 0440302. The terraiin slopes towards the
lake seen in the upper part of the photo. The lake is ca. 141 m a.s.l and
the terrain raises up to 165 m. There are steep areas near the lake (cliffs,
rocky terrain, sparsely old pine trees).
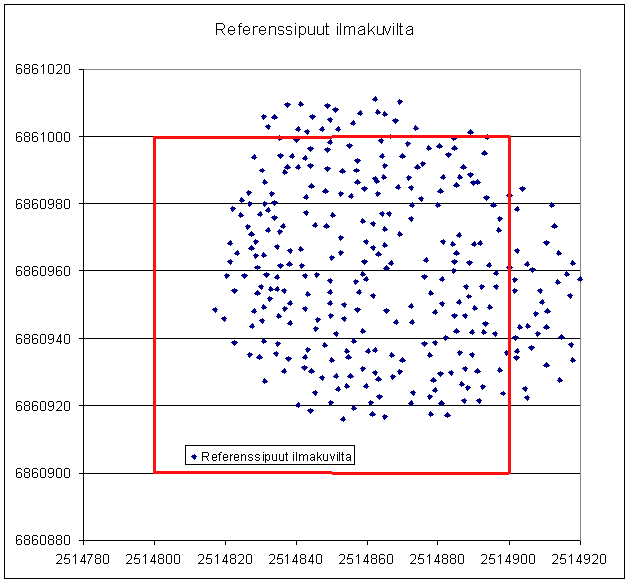
Kuva: Referenssipuut (312) karttana. The reference
treetop on an XY map.
Matlab-pintamallit
Muokkasin Juhan do_DTM_CHM.m ja find_trees.m Matlab-tiedostoja
(kts alla) ja yhdistin ne yhdeksi
komentotiedostoksi, joka lukee hehtaarin lidar-pulssit (pisteet), muodostaa
DTM-, DSM-, ja CHM-pinnat sekä etsii puiden latvoja CHM:n lokaaleina
maksimeina. DTM kirjoitetaan binääriseksi tiedostoksi, jonkA voi
lukea KUVAMITT-ohjelmaan. Binääriselle DTM:lle tulostetaan "kaveriksi"
ASCII HDR-tiedosto. Saadut latvat kirjoitetaan ASCII-tiedostoksi (puutiedosto),
jonka voi lukea KUVAMITT-ohjelmaa ja projisoida latvat. Lopuksi rutiini
tarkistaa yksinkertaisella menetelmällä, mitkä puut tulivat
löydetyiksi sekä piirtää tasossa ja 3D kyseisille puille
paikannusvirhevektorit (quiver-funktio). I edited Juha's
Matlab sample m-files do_DTM_CHM.m and find_trees.m and combined them into
one m-file. In it, the lidar data is read, surfaces: DTM, DSM and CHM are
formed, and tree tops are found based on the assumption that they are represented
by local maxima of the CHM. The DTM is stored into a binary file compatible
with KUVAMITT (with hdr-file). The treetops are stored into an ASCII file,
which is compatible with KUVAMITT, and KUVAMITT can be used for projecting
the points on aerial images for visual check. Finally, the m-file performs
a crude evaluation and produces information about omission and commission
errors and positioning accuracy. Quiver-function is used for displaying results
in 2D and 3D.
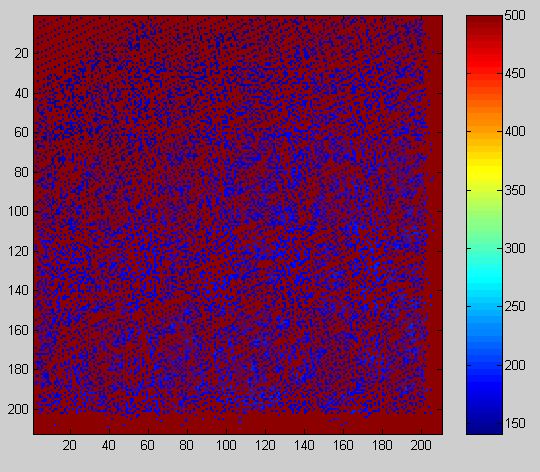
Kuva: osa(), "minimipinta", jossa reiät (puuttuvat havainnnot)
ovat tasolla 500 m. Visualization of array osa(),
which has no-data values at 500 m a.s.l.
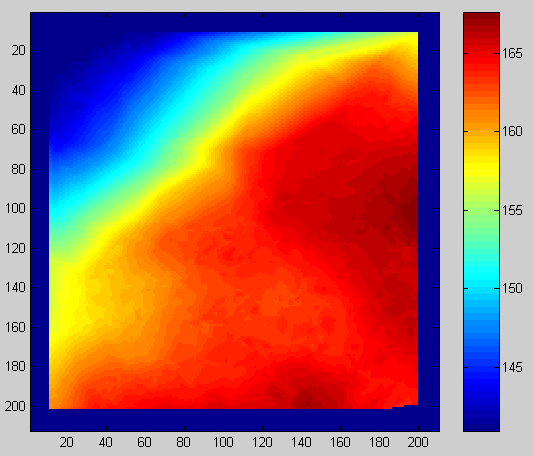
Kuva: Maastomalli: dtm(), 21x21 ja 11x11 naapurustoilla suodatettu
versio. Visualization of array dtm().
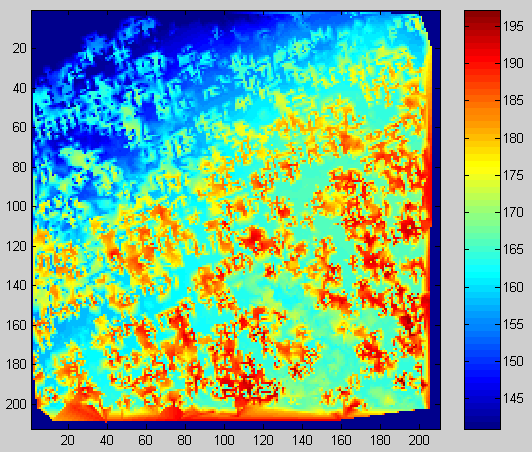
Kuva: dsm(); maksimeista suodatettu (griddata-funktio) pintamalli. Array dsm(), filtered with griddata() -function.
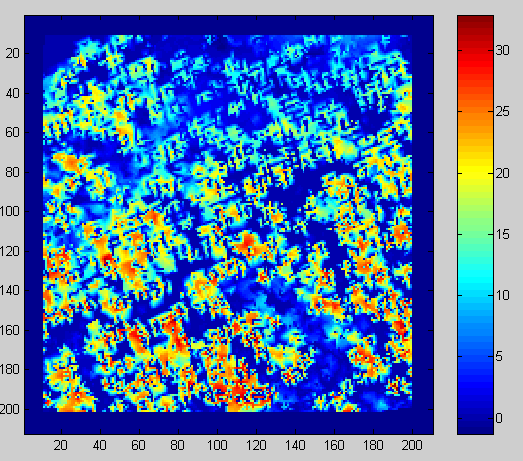
kuva: chm() = dsm()-dtm(). Normalisoituu pintamalli = latvuston korkeusmalli.
Normalized DSM i.e. CHM.
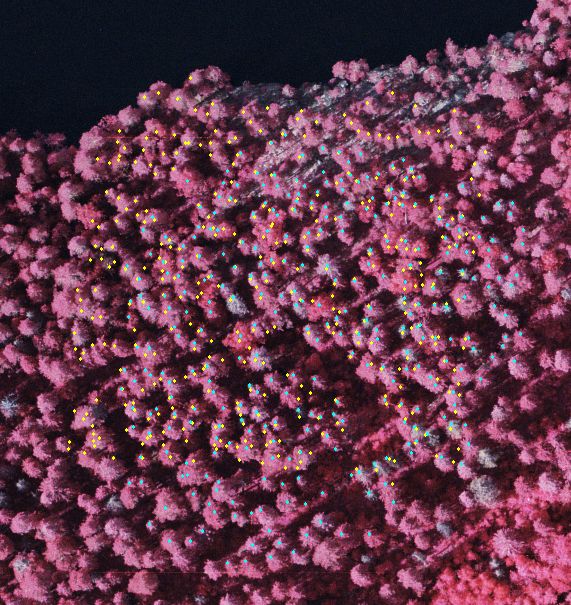
Kuva: Lidar-CHM :n lokaaleista maksimeista saadut latvapisteet projisoituna
(CTRL-Q -toiminto KUVAMITT-ohjelmassa) ilmakuvalle (keltaiset) sekä
referenssipuut (siniset) (modifioitu CTRL-P-toiminto). The lidar CHM maxima superimposed in an aerial view (yellow
dots) and the reference tre tops in blue.
.
Kun KUVAMITT-ohjelmaan oli luettuna lidarista TerraModeler -ohjelmalla
konstruoitu DTM (HydeLidarDTM.hdr), oli puiden tyvien (eli Matlab-koodilla
lasketun dtm-pinnan) korkeustarkkuus RMSE-virheenä mitaten 0.46 m, olettaen,
että Terralla laskettu
malli "on oikea".The Matlab dtm-values (for the "trees"
found in the lidar data ) had an RMSE of 0.46 m when compared with
the DTM obtained with TerraModeler (giving RMSE we must assume that the Terramodeler
model is correct!)
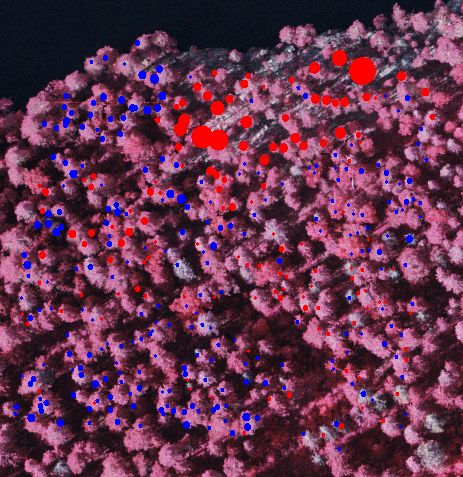
Kuva: Juhan koodilla tuotetun DTM:n ja TErraModeler-ohjelmalla lasketun
HydeLidarDTM.Hdr erot (610 pistettä, h > 10 m). Punainen väri
indikoi, että HydeLidarDTM.Hdr on korkeammalla. Suurin ero on -3.04
m. Matlab-koodi on "syönyt rinnettä". Differences
between the matlab-dtm (modified Wack, as Juha called it) and the DTM produced
with TerraModeler-software. 610 points (lidar trees). Largest difference
is -3.04 m, the matlab-dtm underestimates elevation in the slopes ("it eats
up the terrain"). Again, we do not know if the TerraModeler DTM is actually
any better, because true reference is missing!
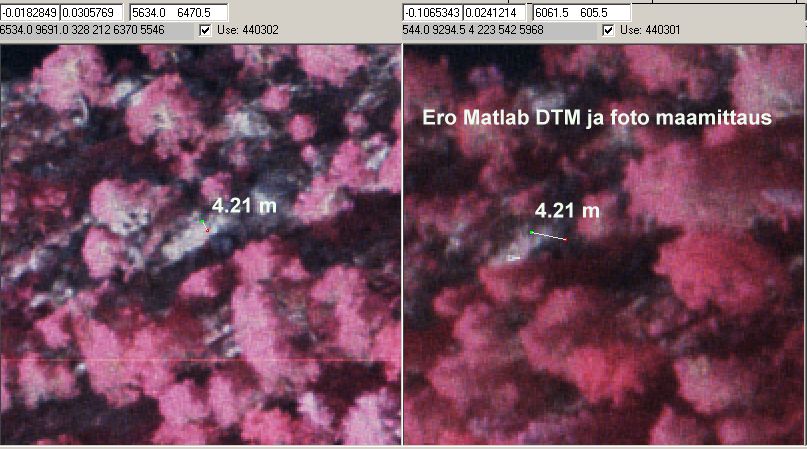
Kuva: Maanpinnan fotogrammetrisen korkeuden ja Matlab-DTM:n ero oli 4.2
m rinteessä. Samassa paikassa ero TerraModeler-malliin oli 1.8 m eli
ei sekään vaikuta huipputarkalta. Inplaces
the terrain is visible in aerial views. Here, the matlab dtm is off by 4.21
m in comparison to photogrammetric Z. For the same point, the TerraModeler-DTM
was off by 1.8 m, so if the the photogrammetric observation really applies
ground, neither of the DTMs is quite correct.
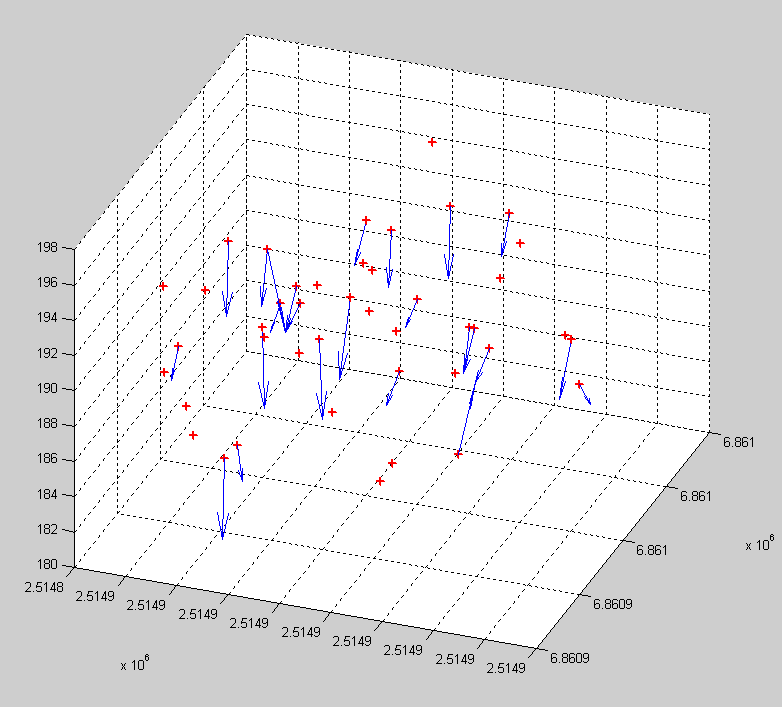
Kuva: Säteeltään 20-metrisen ympyräkoealan sisällä
on referenssilatvoja (+), joille on löydetty lidar-CHM-maksimi. Sininen
vektori osoittaa ko. pisteeseen. Kuvasta näkee, kuinka mätsäysalgoritmi
sallii duplikaatit, eli samaan puuhun sallitaan useampi osuma. Lidar-osumat
ovat tosilatvojen alta. The matlab-code displays the
reference tree tops (+ signs) and "lidar-found trees" in 3D. The blue
vectors point to the lidar-tree tops which map to the particular tree. The
matching algorithm allows for duplicates (vectors pointing to the same point),
which is not very clever.











